


THR involves surgically removing the arthritic parts of the joint (cartilage and bone), replacing the "ball and socket" part of the joint with artificial components made from metal alloys (Titanium/ Cobalt-chrome), and placing high-performance bearing surface between the metal parts. Most commonly, the bearing surface is made from a very durable polyethylene plastic, but other materials (including ceramics, newer plastics, or metals) have been used. Most patients will walk with a walker or crutches for 2 to 3 weeks, most will use a cane for another 2 to 3 weeks after that; after that, the large majority of patients are able to walk freely. You can get treated from the best hip replacement surgeon in Delhi at Dr. Gurdeep Singh Ratra Clinic.
There are two major types of artificial hip replacement treatment:
1) Cemented prosthesis
2) Uncemented prosthesis
A Cemented Prosthesis is held in place by bone cement that attaches the metal to the bone.
An Uncemented Prosthesis bears a fine porous coating on the surface that allows bone to grow into the coating and attach the prosthesis to the bone.
The decision about whether to use a cemented or uncemented artificial hip is usually made by the surgeon based on your age and lifestyle, and the surgeon's experience. Each prosthesis is made of two main parts. The acetabular component (socket) replaces the acetabulum. The acetabular component is made of a metal shell with a plastic inner liner that provides the bearing surface. The femoral component (stem and ball) replaces the femoral head. The femoral component is made of metal.
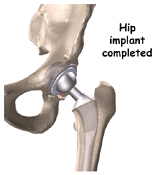
The Operation
The surgeon begins by making an incision on the side of the thigh to allow access to the hip joint. Once the hip joint is entered, the surgeon dislocates the femoral head from the Acetabulum . Then the femoral head is removed by cutting through the femoral neck with a power saw.
Attention is then turned toward the socket. The surgeon uses a power drill and a special reamer (a cutting tool used to enlarge or shape a hole) to remove cartilage from inside the acetabulum. The surgeon shapes the socket into the form of a half-sphere. This is done to make sure the metal shell of he acetabular component will fit perfectly inside.
To begin replacing the femur, special rasps (filing tools) are used to shape the hollow femur to the exact shape of the metal stem of the femoral component. Once the size and shape are satisfactory, the stem is inserted into the femoral canal. Again, in the uncemented variety of femoral component the stem is held in place by the tightness of the fit into the bone. In the cemented variety, the femoral canal is enlarged to a size slightly larger than the femoral stem, and the bone cement is used to bond the metal stem to the bone. Once the surgeon is satisfied that everything fits properly, the incision is closed with stitches.
What happens after surgery?
After surgery, your hip will be covered with a padded dressing. A triangle-shaped cushion may be positioned between your legs to keep your legs from crossing or rolling in. Physical therapy treatments are scheduled one to three times each day as long as you are in the hospital. Your therapist will begin by helping you move from your hospital bed to a chair. By the second day, you'll begin walking longer distances using your crutches or walker. Most patients are safe to put comfortable weight down when standing or walking. However, if your surgeon used a noncemented prosthesis, you may be instructed to limit the weight you bear on your foot when you are up and walking. Your therapist will review exercises to begin toning and strengthening the thigh and hip muscles. Ankle and knee movements are used to help pump swelling out of the leg and to prevent the formation of blood clots.
Rehabilitation
After you are discharged from the hospital, your therapist may see you for one to six in-home treatments. Your therapist will review your exercise program, continue working with you on your hip precautions, and make recommendations about your safety. These safety tips include using raised commode seats and bathtub benches, and raising the surfaces of couches and chairs. This keeps your hip from bending too far when you sit down. You should use your walker or crutches as instructed. If you had a cemented procedure, you'll advance the weight you place through your sore leg as much as you feel comfortable. If you had a noncemented procedure, your surgeon may want you to place only the toes of your operated leg down for up to six weeks after surgery. Most patients progress to using a cane in three to four weeks. Your staples will be removed two weeks after surgery. Your therapist may use heat, ice, or electrical stimulation to reduce any swelling or pain.
FAQs ABOUT HIP REPLACEMENT TREATMENT
.jpg)
Normal hip joint anatomy:
The hip joint is a ball and socket joint formed between the head of the thigh bone (femur) and the hip bone (pelvis).
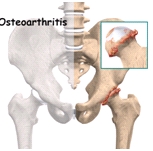
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is a condition caused by breakdown of cartilage. Cartilage is a protein substance that normally serves as a cushion between bones of a joint. Primary osteoarthritis is related to ageing and is rarer in Indians than in the west. With ageing, the water content of the cartilage changes and protein makeup degenerates, gradually leading to a loss of cartilage cushion between joint bones. This causes friction between bones, leading to pain and limitation of joint mobility.
What causes hip pain?
Osteoarthritis
Fractures/dislocations
Rheumatoid arthritis
Post infection arthritis
Aseptic bone necrosis / Avascular necrosis
.jpg)
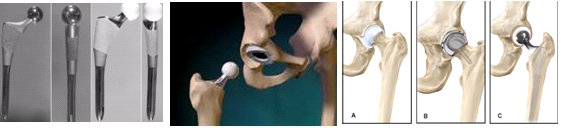
What is a hip replacement treatment?
In a total hip replacement surgery, the painful parts of the damaged hip are replaced with artificial hip parts called a prosthesis, a device that substitutes or supplements a joint. The prosthesis consists of titanium components: a socket, ball, and stem. The outer shell of the socket is usually made of metal and the inner shell consists of plastic, or the entire socket may be plastic. When the metal ball is joined with the socket, the new hip can allow for smooth, nearly frictionless movement.
How is the implant affixed in the body?
The decision as to whether to use a cemented or press-fit component depends upon many factors, including the manufacturer’s intended use of the product, surgeon philosophy and the patient’s condition.

What are the types of replacement options?
Cemented, non-cemented, hybrid, surface replacement, metal-on-polyethylene, ceramic-on-ceramic, metal-on-metal depending on indication, patient profile and surgeon’s discretion.
What can you expect after surgery?
When you are back in your hospital room you will begin a gentle rehabilitation program to help strengthen the muscles around your new hip and regain your range of motion. On the day of surgery you may be asked to sit on the edge of the bed and dangle your feet. You will also learn how to protect your new hip while doing daily activities. As soon as possible, usually within the next 24 hours, your physical therapist will help you start walking a few steps at a time. As you heal you will progress from walker to crutches and then a cane. Before you are discharged from the hospital, an occupational therapist will also show you how to perform daily tasks at home with your new hip. For example, he or she will instruct you on how to go to the bathroom, how to dress yourself, how to sit or stand, how to pick up objects and many others.
How long does the patient have to stay in hospital?
1-2 days before surgery to 3-5 days after surgery. This is to provide pain relief, anticoagulant prophylaxis and patient ambulation
When and how can you walk after surgery?
The patient is made to walk 24-48 hours after surgery. Weight bearing maybe delayed for 3-4 weeks in non-cemented implants. Crutches or walker are used to aid ambulation for 3-4 weeks, then a cane for another 3-4 weeks. So, you can walk without any support after 1 ½ to 2 months.
What implants are used?
We use only standard prostheses made in USA. These are imported to India by the same companies that operate worldwide- Zimmer, Depuy (Johnson & Johnson), Biomet.
Is hip replacement treatment painful?
Post operative pain is controlled to tolerable levels by excellent multi-modal anaesthesia, epidural block and patient controlled analgesia. Initial injectable painkillers is replaced by oral tablets within 2-3 days.
How long does the surgery take?
Anaesthesia induction time is 20 to 30 minutes. A primary replacement takes 30 to 60 minutes. A difficult, badly deformed, stiff hip or a revision surgery may take 2 to 3 hours.
For how many years is my replacement expected to last?
A well done THR lasts 20-30 years, after which it may need revision, which itself is a successful procedure.
What kind of physical activity can you do after surgery?
You can walk as much as you want. You can climb stairs, drive a car, and even gradually go back to non-contact sports like golf.
When can the patient go back to work?
This depends on the job. A sedentary or desk job person can return to work in about a month. If the work involves a lot of walking or standing, then about 2 months.
Can you travel overseas after the operation?
For overseas patients, it can be done 3-4 weeks after surgery. Any patient can safely go abroad 2 months after surgery.
What precautions should you take after a THR?
Avoid squatting, sitting cross legged, using a low chair or an Indian toilet. Do not ignore any infection (dental, skin or otherwise)- consult a doctor in case of any infection.
Photos & Video Gallery
| PHOTOS | ||
|
Model |
Pre operative X-Ray |
Model |
|
Post Operative X-Ray Cemented Hip Replacement |
Pre Operative X-Ray |
Post Operative X-Ray Non Cemented Hip Replacement |
|
X-Ray Hip Resurfacing |
Reverse Shoulder |
Shoulder Replacement |
|
Ankle Replacement |
Ankle Replacement |
|